Navigating the Future with Data Management as a Service (DMaaS)

Audio : Listen to This Blog.
In today’s exponentially growing digital landscape, the ability to manage vast amounts of data efficiently is not just an operational need but a strategic asset. For CXOs, IT Managers, and Software Engineers, understanding the nuances of Data Management as a Service (DMaaS) can be the difference between leading in their industry or lagging. This blog post aims to demystify DMaaS, outlining its benefits, key features, use cases, challenges, and future of this innovative service.
Introduction to Data Management as a Service (DMaaS)
Data Management as a Service represents a cloud-based approach to data integration, storage, and analytics. It provides organizations with comprehensive capabilities to handle large volumes of data from diverse sources without needing on-premises infrastructure. By leveraging DMaaS, businesses can focus on extracting value from their data rather than managing data storage and maintenance complexities.
Leveraging Data Management as a Service entails a strategic realignment of focus for businesses. They shift their attention away from the intricacies of data storage and maintenance towards the more lucrative pursuit of deriving actionable insights and value from their data assets. At its core, DMaaS redefines the traditional data management landscape, offering a holistic suite of capabilities tailored to the complexities of modern data ecosystems.
Through streamlined cloud-based operations, DMaaS facilitates seamless data integration and storage, enabling enterprises to transcend the limitations of physical infrastructure. Consequently, businesses can allocate resources more efficiently, directing efforts towards leveraging advanced analytics techniques to uncover meaningful patterns and trends within their datasets, thereby unlocking the untapped potential for innovation and competitive advantage.
Key Features and Components of Data Management as a Service
DMaaS is characterized by several key features that make it an indispensable tool for modern organizations. These include:
1. Multi-cloud and Hybrid Cloud Support
Ensuring seamless data management across various cloud environments is crucial for organizations utilizing a combination of public, private, and hybrid clouds. DMaaS achieves this by offering a unified platform to manage data dispersed across cloud providers and on-premises data centers. This enables businesses to leverage the full potential of their data, regardless of where it resides, ensuring flexibility and optimizing costs associated with data storage and management.
2. Data Integration and Analytics
Another vital aspect of DMaaS is providing tools for integrating data from multiple sources and extracting actionable insights. This feature allows organizations to consolidate disparate data forms into a coherent framework, including structured and unstructured data. Advanced analytics capabilities are applied to this integrated data, enabling businesses to derive meaningful insights that can inform decision-making processes, improve operational efficiency, and drive innovation.
3. Automated Backups and Recovery
Offering robust disaster recovery solutions to minimize data loss is essential for business continuity. DMaaS platforms usually include automated backup and recovery features, which periodically save copies of data across different locations. This redundancy allows users to quickly restore data in the event of hardware failure, cyberattacks, or other types of data loss incidents, significantly reducing downtime and the associated costs.
4. Scalable Storage Solutions
Thanks to DMaaS’s cloud-based nature, businesses can scale their storage needs without physical constraints. This scalability allows for accommodating growing data volumes without upfront investment in physical storage infrastructure. Organizations can adjust their storage resources dynamically, ensuring that they only pay for what they use and can easily expand their capacity as their needs evolve.
5. Compliance and Security
Implementing stringent security measures and compliance protocols to protect sensitive information is a fundamental component of DMaaS. Given the increasing prevalence of cyber threats and the growing regulatory landscape, DMaaS providers incorporate advanced security technologies and best practices to safeguard data. This includes encryption, access controls, regular security audits, and adherence to international standards and regulations to ensure data handling practices meet compliance requirements.
Benefits of Data Management as a Service
Source: Cloud Patterns
The adoption of DMaaS represents a strategic imperative for organizations seeking to capitalize on the benefits of cloud-based data management while mitigating the inherent challenges of traditional on-premises solutions. By embracing the scalability, cost efficiency, and security features offered by DMaaS, businesses can unlock new opportunities for innovation, accelerate time-to-insight, and gain a competitive edge in today’s data-driven economy.
1. Scalability and Elasticity
DMaaS offers unparalleled scalability and elasticity, allowing organizations to scale their data management resources up or down in response to changing demand. With cloud-based infrastructure, businesses can dynamically adjust storage capacity, computing power, and data processing resources as needed, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
2. Cost Efficiency and Predictability
By adopting DMaaS, organizations can significantly reduce capital expenditures associated with hardware procurement, maintenance, and upgrades. With a pay-as-you-go pricing model, businesses only pay for the resources they consume, enabling predictable budgeting and cost management. This cost-efficient approach eliminates the need for upfront investments in infrastructure while providing flexibility to scale resources based on actual usage patterns.
3. Enhanced Data Security and Compliance
DMaaS providers implement robust security measures and compliance frameworks to safeguard sensitive data against unauthorized access, breaches, and regulatory violations. Through encryption, access controls, and regular audits, businesses can ensure their data’s integrity, confidentiality, and availability, thereby mitigating risks and maintaining regulatory compliance. By entrusting their data management to reputable DMaaS providers, organizations can build trust with customers, partners, and regulators, reinforcing their commitment to data protection and privacy.
4. Improved Data Accessibility and Availability
DMaaS makes data more accessible and available to users across the organization, regardless of their location or device. Cloud-based storage and integration solutions enable seamless access to data from any internet-connected device, facilitating collaboration, decision-making, and innovation. By breaking down silos and enabling real-time access to data, DMaaS empowers businesses to extract actionable insights and drive informed decision-making at every level of the organization.
5. Streamlined Data Integration and Management
DMaaS simplifies data integration and management complexities, providing organizations with tools and frameworks to streamline data ingestion, transformation, and governance processes. Through pre-built connectors, APIs, and data pipelines, businesses can seamlessly integrate data from disparate sources, enabling a single source of truth for analysis and reporting. This streamlined approach reduces time-to-insight, minimizes errors, and enhances data quality, empowering organizations to derive maximum value from their data assets.
6. Agility and Innovation
With DMaaS, organizations gain the agility and flexibility to experiment with new data-driven initiatives, technologies, and business models. Cloud-based infrastructure and services enable rapid prototyping, development, and deployment of innovative solutions, accelerating time-to-market and fostering a culture of continuous innovation. By leveraging DMaaS capabilities, businesses can adapt swiftly to changing market dynamics, seize emerging opportunities, and stay ahead of the competition in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
7. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
DMaaS offers robust disaster recovery and business continuity capabilities, ensuring the resilience and availability of critical data and applications during unforeseen disruptions or disasters. Cloud-based backup and replication services enable automated, geo-redundant data protection, minimizing downtime and data loss risks. With built-in failover mechanisms and recovery options, businesses can maintain continuity of operations, mitigate financial losses, and safeguard their reputation in the face of adversity.
Use Cases and Applications of Data Management as a Service

DMaaS finds application across various sectors, demonstrating its versatility. Organizations dealing with large amounts of data can benefit from DMaaS’s services, harnessing its scalable storage, integrated analytics, and robust data protection to enhance operational efficiency and decision-making capabilities.
Healthcare: Data Management as a Service (DMaaS) is critical in securely managing vast patient records and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations such as HIPAA. By centralizing patient data in a secure cloud environment, healthcare providers can streamline access to medical records, enabling timely and informed decision-making by healthcare professionals.
FinTech: DMaaS is instrumental in enabling real-time fraud detection and compliance monitoring to mitigate risks and ensure regulatory compliance within the financial services industry. By leveraging DMaaS solutions, financial institutions can aggregate and analyze vast amounts of transactional data from multiple sources in real-time, enabling them to identify suspicious activities and fraudulent transactions promptly.
Retail: Businesses harness the power of DMaaS to gain deeper insights into customer behavior and preferences, driving personalized shopping experiences and enhancing customer satisfaction. By analyzing vast amounts of real-time transactional and customer data, retailers can identify trends, predict consumer preferences, and optimize pricing and product recommendations.
Education: DMaaS facilitates efficient student data management, academic records, and administrative processes. Educational institutions can leverage DMaaS solutions to centralize student information, streamline enrollment processes, and enhance collaboration among faculty and staff.
Manufacturing: DMaaS empowers organizations to optimize production processes, improve supply chain visibility, and enhance product quality. By integrating data from IoT sensors, equipment, and supply chain systems, manufacturers can gain real-time insights into production metrics, identify potential bottlenecks, and proactively address maintenance issues.
Energy: DMaaS is crucial in optimizing energy generation, distribution, and consumption processes. Energy companies can utilize DMaaS solutions to aggregate data from smart meters, grid sensors, and renewable energy sources, enabling real-time monitoring and management of energy assets.
Challenges and Considerations
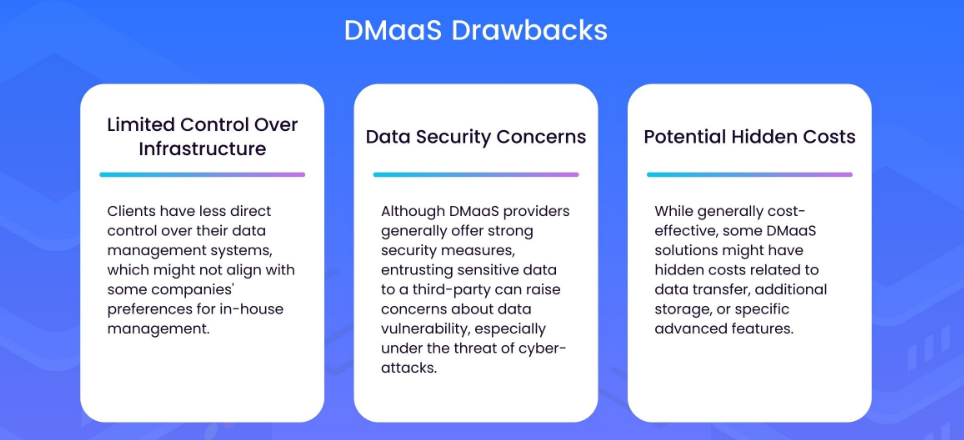
Source: Resmo
Data sovereignty and privacy concerns are paramount, requiring organizations to meticulously choose DMaaS providers that adhere to regional and international regulations, like GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California. The technical sophistication of DMaaS solutions necessitates that businesses possess or develop advanced in-house capabilities. This includes familiarity with API integrations, a thorough understanding of cloud architecture, and data analytics and security protocols expertise.
Essential tools like Terraform for cloud infrastructure as code, Kubernetes for container orchestration, and Apache Kafka for real-time data streaming might be integral to leveraging DMaaS effectively. Interoperability with legacy systems presents another layer of complexity. Organizations must assess the extent to which a DMaaS can integrate with existing IT ecosystems, possibly requiring middleware or custom-developed adapters.
Vendor lock-in is a significant risk, with proprietary technologies or platforms potentially limiting future flexibility. Strategies to mitigate this risk include adopting open standards and technologies where possible and considering multi-cloud DMaaS solutions that avoid dependence on a single provider’s ecosystem.
Future Trends and Outlook
The future of DMaaS is bright, with several trends indicating its increasing importance. The rise of edge computing and IoT devices will generate even more data, further emphasizing the need for efficient data management solutions. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning integrations within DMaaS platforms are expected to enhance data analytics capabilities, offering deeper insights and predictive analytics. Furthermore, as concerns around data privacy heighten, DMaaS providers will likely introduce more advanced security features to meet these demands.
1. Edge Computing and IoT Expansion
The proliferation of edge computing and Internet of Things (IoT) devices is poised to fuel exponential growth in data generation. This surge in data volume underscores the critical importance of efficient data management solutions like DMaaS to handle and process data closer to its source.
2. Integration of AI and Machine Learning

Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) capabilities within DMaaS platforms is set to revolutionize data analytics. These advanced technologies enable more sophisticated data processing, facilitating deeper insights, pattern recognition, and predictive analytics, empowering organizations to make data-driven decisions more accurately and quickly.
3. Enhanced Data Security Measures

As data privacy concerns continue to mount, DMaaS providers are expected to bolster their security measures to safeguard sensitive information. Anticipated advancements include implementing robust encryption techniques, access controls, and data anonymization methods to ensure compliance with stringent data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Wrap-Up

Data Management as a Service transforms how organizations approach data storage, integration, and analysis. DMaaS enables businesses to focus on extracting value from their data by offering a scalable, cost-effective, and secure solution. Despite the challenges, the strategic adoption of DMaaS positions organizations to better manage the complexities of the modern data landscape and harness the power of their data assets. For CXOs, IT Managers, and Software Engineers, staying informed about DMaaaS developments is crucial to successfully navigate the future of data management.
